This is a core topic in electronics. I’ll teach it in two clear parts:
👉 Part 1: Semiconductor Physics
👉 Part 2: Diodes
👉 What is a Semiconductor?
A semiconductor is a material whose electrical conductivity is between conductor and insulator.
Main examples:
✅ Silicon (Si)
✅ Germanium (Ge)
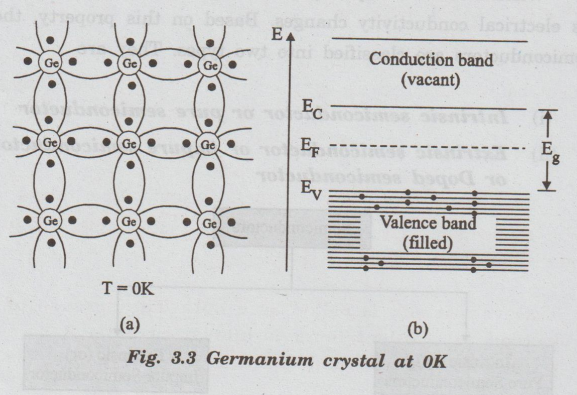
🔹 Intrinsic Semiconductor
A pure semiconductor without impurities.
Properties:
- Equal number of electrons and holes
- Conductivity is low
- Depends on temperature
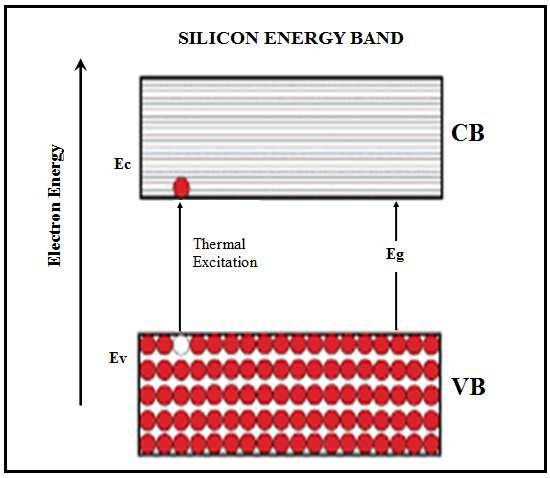
When heat is applied:
👉 Electrons jump to conduction band
👉 Holes are created in valence band
These electron-hole pairs carry current.
🔹 Extrinsic Semiconductor (Doping)
When impurities are added to increase conductivity.
1. N-type Semiconductor
- Doped with pentavalent atoms (P, As)
- Extra electrons are majority carriers
2. P-type Semiconductor
- Doped with trivalent atoms (B, Al)
- Holes are majority carriers
👉 Doping increases conductivity.
⚡ Current in Semiconductors
Current flows due to:
- Movement of electrons
- Movement of holes
Both contribute to electric current.
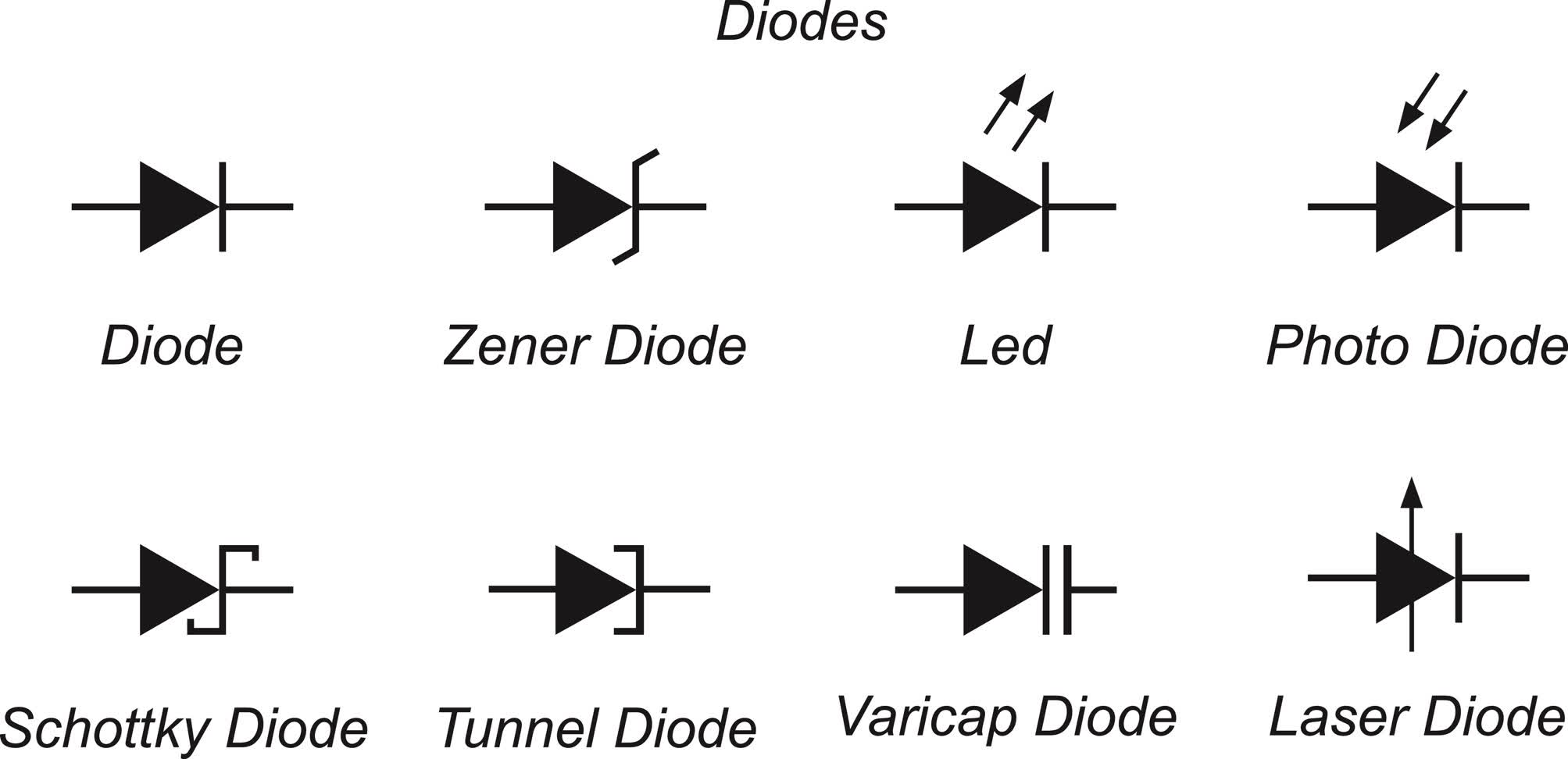
🔋 Semiconductor Diodes
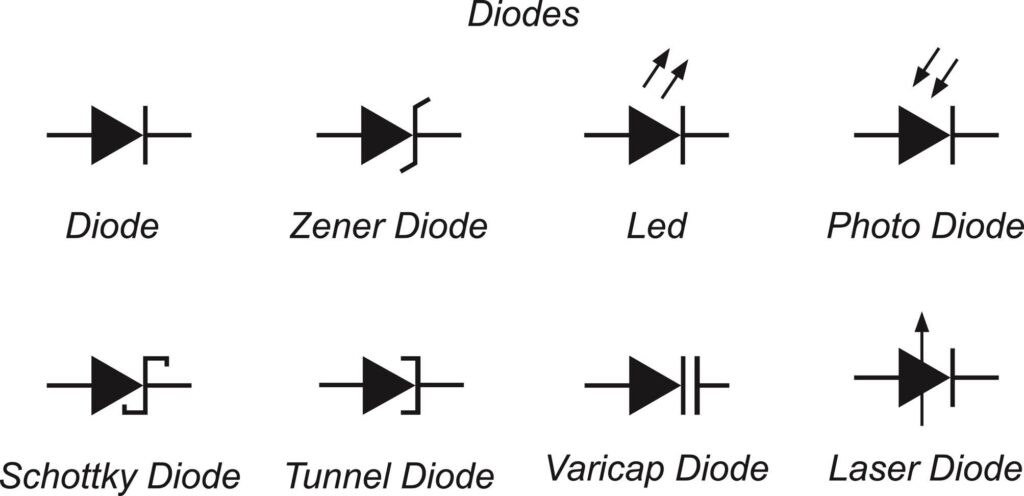
👉 What is a Diode?
A diode is a PN junction device that allows current to flow in one direction only.
It is formed by joining:
👉 P-type + N-type semiconductor
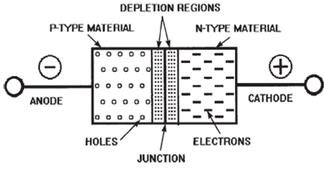
🔹 PN Junction Formation
When P and N regions join:
- Electrons and holes recombine
- A depletion region is formed
- An electric field is created
This region controls current flow.
🔹 Forward Bias
When:
👉 P-side → positive terminal
👉 N-side → negative terminal
Result:
- Depletion region decreases
- Current flows easily
🔹 Reverse Bias
When:
👉 P-side → negative
👉 N-side → positive
Result:
- Depletion region increases
- Very small current flows
🔹 Applications of Diodes
- Rectifiers (AC to DC conversion)
- Signal detection
- Voltage regulation
- LED lighting
🧠 Short Exam Summary
👉 Semiconductors have moderate conductivity controlled by doping.
👉 Intrinsic semiconductors are pure; extrinsic are doped.
👉 A diode is a PN junction that conducts in forward bias and blocks in reverse bias.
Classification of Electronic Components click here…
Classification of Materials in Electronics click here…