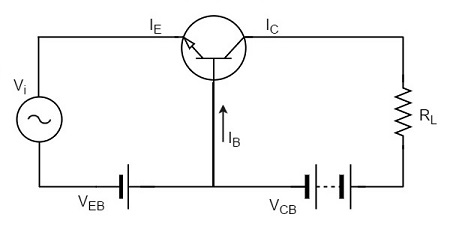
👉 What is a Transistor Amplifier?
A transistor amplifier is a circuit that increases the strength (amplitude) of a weak signal using a transistor.
👉 It converts a small input signal into a large output signal.
Example: Microphone signal → Speaker sound
🔹 Basic Principle of Amplification
A transistor works as an amplifier when it is operated in the active region.
👉 Small change in base current
➡ produces large change in collector current
➡ results in amplified output voltage
So:
👉 Small input → Large output
🔹 Common Emitter (CE) Amplifier
Most widely used amplifier.
Features:
- High voltage gain
- Moderate current gain
- 180° phase shift between input & output
Working:
- Input signal is applied to base-emitter
- Output is taken from collector-emitter
- Coupling capacitors block DC and pass AC signal
🔹 Types of Transistor Amplifiers
1. Common Emitter (CE)
- High gain
- Most popular
2. Common Base (CB)
- High voltage gain
- Low input resistance
3. Common Collector (CC) (Emitter Follower)
- High current gain
- Used for impedance matching
🔹 Gain of Amplifier
Voltage Gain:
Av=Input VoltageOutput Voltage
Higher gain = stronger amplification.
🔹 Applications
- Audio amplifiers
- Radio and TV circuits
- Communication systems
- Signal processing
Semiconductor Physics and Diodes click here…
Diode applications and other terminal devices click here…
Classification of Electronic Components click here…