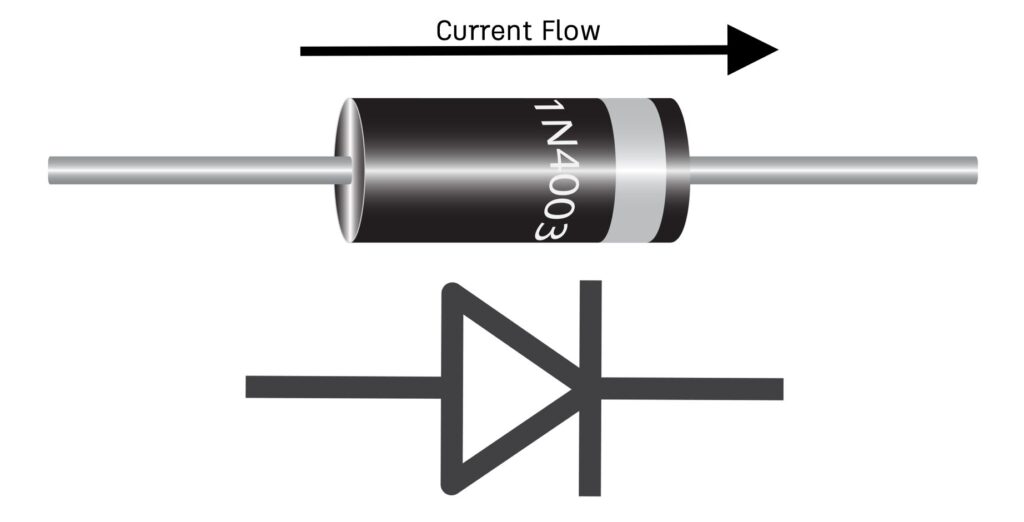
Now we’re moving to practical electronics. I’ll explain in two parts:
👉 1. Applications of Diodes
👉 2. Other Terminal Devices
🔋 Applications of Diodes
Diodes are used in many electronic circuits because they allow one-way current flow.
🔹 1. Rectification (AC → DC)
- Diodes convert AC into DC
- Used in power supplies
- Types: Half-wave & Full-wave rectifiers
👉 Example: Mobile charger
🔹 2. Clipping Circuits
- Removes unwanted parts of a signal
- Protects circuits from high voltage
👉 Used in signal processing
🔹 3. Clamping Circuits
- Shifts voltage level of signals
- Maintains waveform shape
👉 Used in TV and communication systems
🔹 4. Voltage Regulation (Zener Diode)
- Maintains constant output voltage
- Protects devices from voltage fluctuations
🔹 5. Light Emission (LED)
- Converts electrical energy to light
- Used in displays and indicators
🔹 6. Detection (Demodulation)
- Extracts information from signals
- Used in radio receivers
⚙️ Other Terminal Devices
(Devices with more than two terminals used for switching/amplification)
🔸 Transistor (BJT)
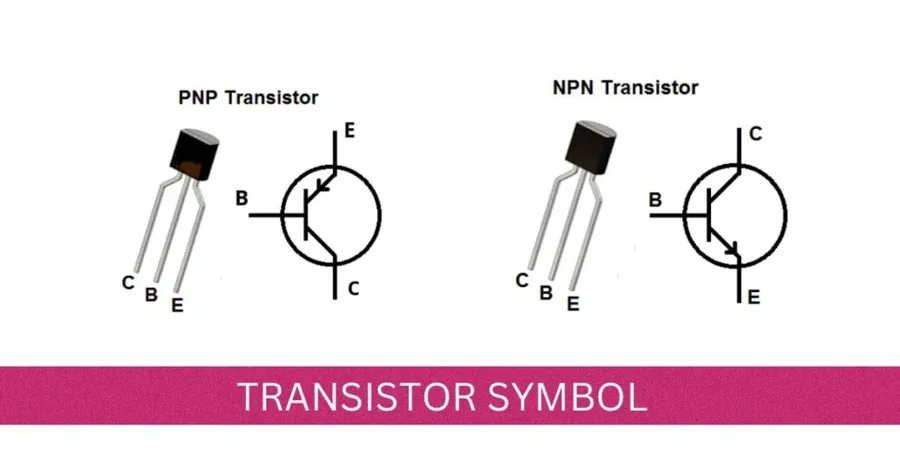
👉 What is a Transistor?
A transistor is a three-terminal semiconductor device.
Terminals:
- Emitter
- Base
- Collector
Functions:
- Amplification
- Switching
Types:
- NPN
- PNP
👉 Used in amplifiers, computers, radios.
🔸 Field Effect Transistor (FET)
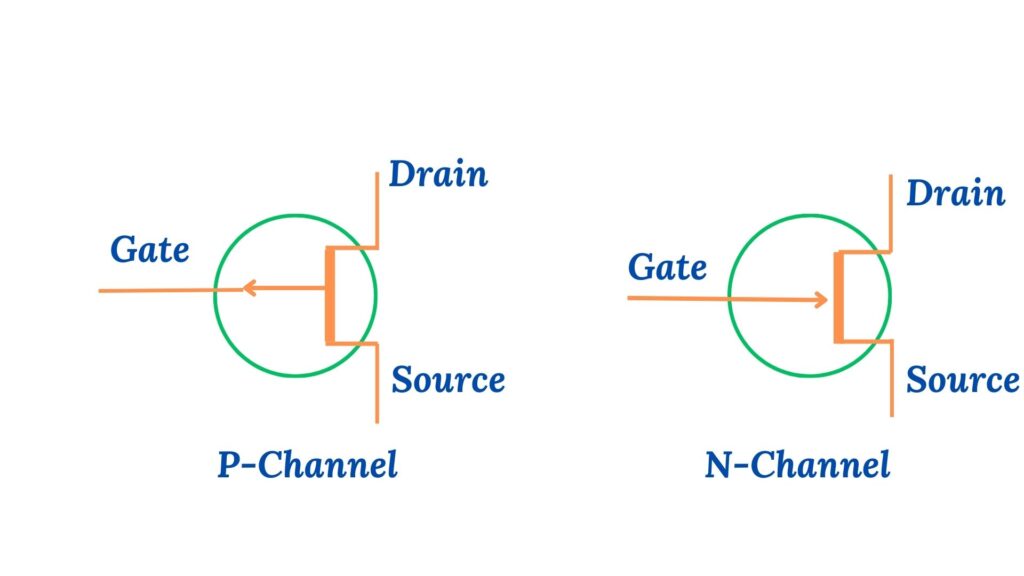
👉 What is FET?
A voltage-controlled device with three terminals:
- Gate
- Source
- Drain
Features:
- High input impedance
- Low power consumption
👉 Used in ICs and digital circuits.
🔸 Thyristor (SCR)
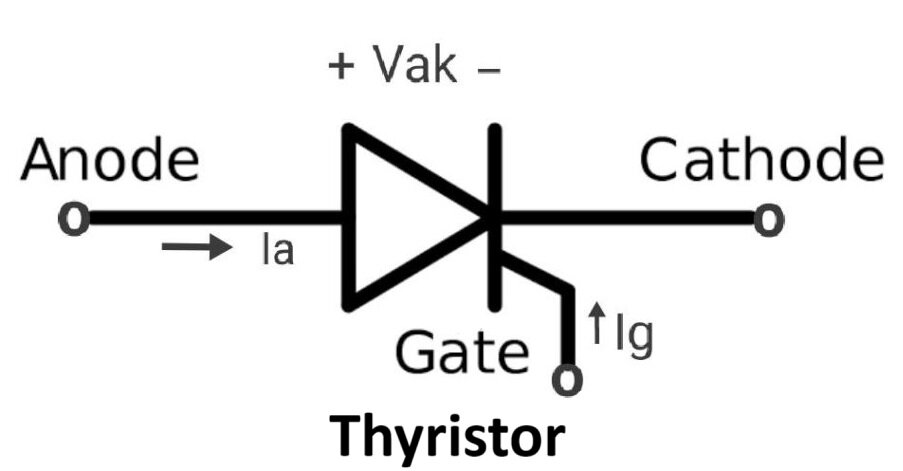
👉 What is SCR?
A four-layer semiconductor device used for power control.
Terminals:
- Anode
- Cathode
- Gate
Applications:
- Motor speed control
- Power regulation
- Light dimmers
🧠 Quick Exam Summary
👉 Diodes are used for rectification, clipping, clamping, and regulation.
👉 Transistors amplify and switch signals.
👉 FETs are voltage-controlled devices.
👉 SCRs control high power circuits.


