🔌 What are Electronic Components?
Electronic components are the basic building blocks of any electronic circuit. They control the flow of electricity to perform useful functions like amplifying signals, storing energy, or switching.
Electronic components are mainly divided into two types:
👉 1. Passive components
👉 2. Active components
⚡ Passive Electronic Components
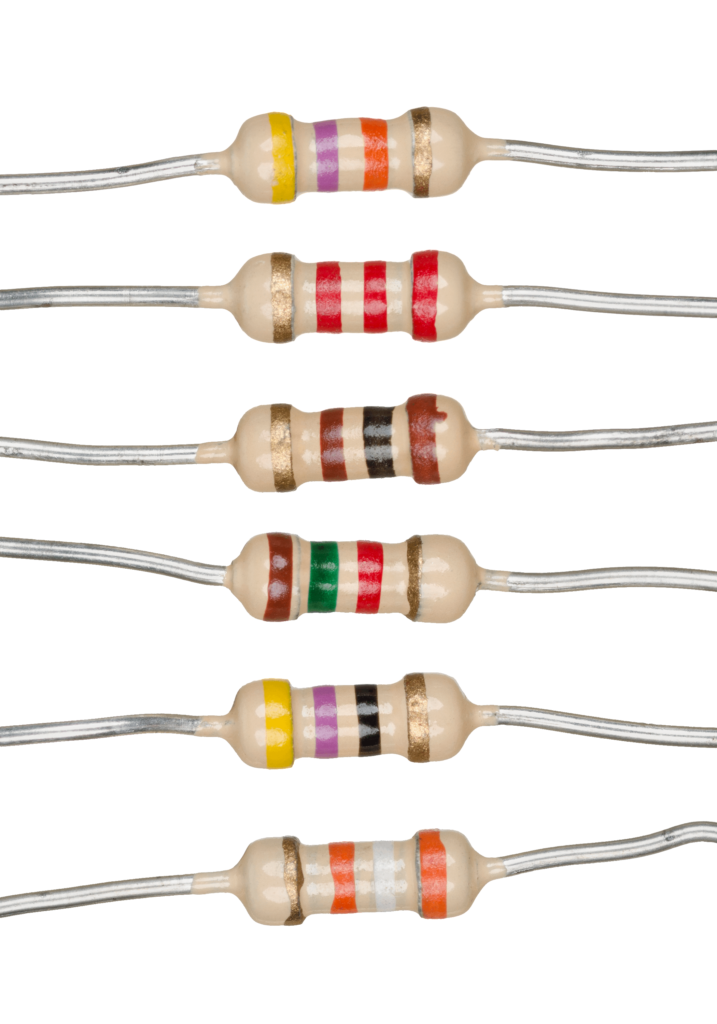

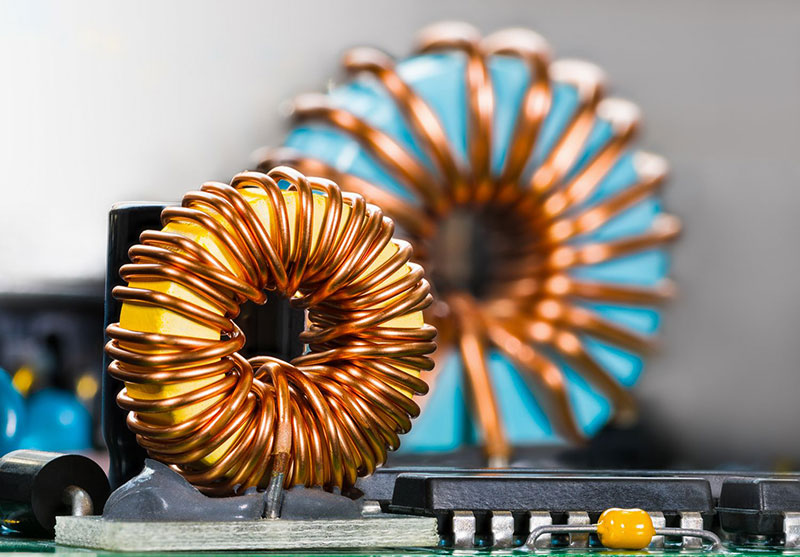
Passive components do not need external power to work. They cannot amplify signals — they only store or control energy.
1. Resistor (R)
- Opposes the flow of electric current
- Measured in Ohms (Ω)
- Used to control voltage and current
👉 Example: Used to protect LEDs from burning.
2. Capacitor (C)
- Stores electrical energy temporarily
- Measured in Farads (F)
- Used in filters and timing circuits
👉 Example: Used in power supplies to smooth voltage.
3. Inductor (L)
- Stores energy in a magnetic field
- Measured in Henrys (H)
- Used in filters and transformers
👉 Example: Used in radio circuits.
🔋 Active Electronic Components
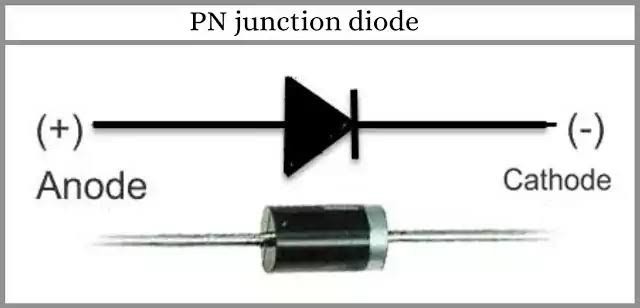
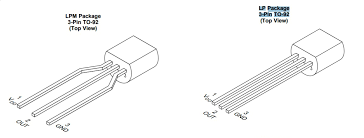
Active components require external power and can amplify or control signals.
1. Diode
- Allows current to flow in one direction only
- Used in rectifiers and protection circuits
👉 Example: LED (Light Emitting Diode)
2. Transistor
- Acts as a switch or amplifier
- Main types: BJT and MOSFET
👉 Example: Used in amplifiers and computers.
3. Integrated Circuit (IC)
- A small chip containing many components
- Used in almost all electronic devices
👉 Example: Microprocessors, timers (like 555 IC)
🧠 Simple Summary (Easy to Remember)
👉 Passive components = control/store energy
👉 Active components = control/amplify signals
Classification of Materials in Electronics click here…


